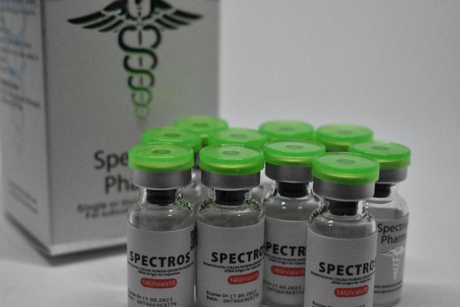
Growth hormone Spectros - pay for quality!!!
Growth hormone and the mechanism of its action
Growth hormone (GH) is a protein produced and secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Of all pituitary hormones, it is produced in the largest amount. The formation and secretion of growth hormone is regulated by hypothalamic releasing hormone and somatostatin. Both of these factors are produced by the hypothalamus. GR is produced throughout life. GH production increases during the period of body growth, approximately up to 20 years, and then decreases with age at an average rate of 14% per decade.
Functions of growth hormone
GR stimulates both linear growth and the growth of internal organs. Causes an increase in the number and size of muscle cells, liver, thymus gland, gonads, adrenal glands and thyroid gland. It affects the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. It inhibits the activity of enzymes that destroy amino acids, increases the level of insulin-like growth factors I and II (IGF I and II) in blood serum, stimulates collagen synthesis in bones, skin, other organs and tissues of the body. GR increases the output of glucose into the hepatic veins, enhances gluconeogenesis (formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors), reduces glucose absorption in the periphery, and also enhances lipolysis (fat breakdown), resulting in an increase in the concentration of free fatty acids in the blood, which suppress the action of insulin on the membrane transport of glucose.
Influence on protein synthesis.
GR stimulates the transport of amino acids into muscle cells and, in addition, enhances protein synthesis, regardless of the effect on the transport of amino acids. In people receiving GR, a positive nitrogen balance occurs, which reflects a general increase in protein synthesis and a decrease in the content of amino acids and urea in plasma and urine. These changes are accompanied by an increase in the level of RNA and DNA synthesis in individual tissues. In this respect, the action of GR is similar to some effects of insulin.
Influence on carbohydrate metabolism.
In terms of influence on carbohydrate metabolism, growth hormone is an antagonist of insulin. Hyperglycemia, which occurs after the introduction of GR, is the result of a combination of reduced peripheral utilization of glucose and its increased production by the liver in the process of gluconeogenesis. Acting on the liver, GR increases the content of glycogen in it, probably due to the activation of gluconeogenesis from amino acids. GR can cause a violation of some stages of glycolysis (breakdown of glucose in tissues) and inhibit glucose transport. Inhibition of the breakdown of glucose in muscles may also be connected with the mobilization of fatty acids from triacylglycerol reserves.
Influence on lipid exchange.
Growth hormone has a powerful lipolytic effect. The processes of lipolysis are intensified with an increase in the mobilization of fat from the depot, which leads to a rapid increase in the concentration of free fatty acids in the plasma and their oxidation in the liver. The energy generated during the increased breakdown of fats is used for anabolic processes in protein metabolism.
The secretion of GH is influenced by a number of stimuli (sleep, stress), and it, like the secretion of many pituitary hormones, is episodic and pulsating in nature. Within a few minutes, the level of GR in the plasma can change 10 times. One of the biggest peaks is noted shortly after falling asleep, which confirms the saying: "He who does not sleep, does not grow." Other stimuli include stress (pain, cold, anxiety, surgical intervention), physical exercise, acute hypoglycemia or starvation, protein food or the amino acid arginine. It is possible that these and many other effectors are related to the main physiological effect of GH, which consists in saving glucose. During stress, hypoglycemia, during sleep or starvation, GR stimulates lipolysis (inflow of fatty acids) and penetration of amino acids (potential substrates of gluconeogenesis) into cells, thus saving glucose for brain metabolism. The release of GH is influenced by many agents, including estrogens, dopamine, alpha-adrenergic compounds, serotonin, opiate polypeptides, intestinal hormones, and glucagon. The point of application of the action of all these factors is the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus, where the regulation of growth hormone secretion is carried out by the feedback type. The short loop of the system includes a positive (stimulating) regulator of secretion - somatoliberin - and a negative (inhibitory) regulator - somatostatin.
See other гормоны роста